(458g) Magnetically Aligned Metal-Organic Deposition (MOD) Ink Based Functional Surfaces with Enhanced Wettability
AIChE Annual Meeting
2022
2022 Annual Meeting
Nanoscale Science and Engineering Forum
Nanoscale Science and Engineering Forum I (All Papers)
Wednesday, November 16, 2022 - 9:54am to 10:13am
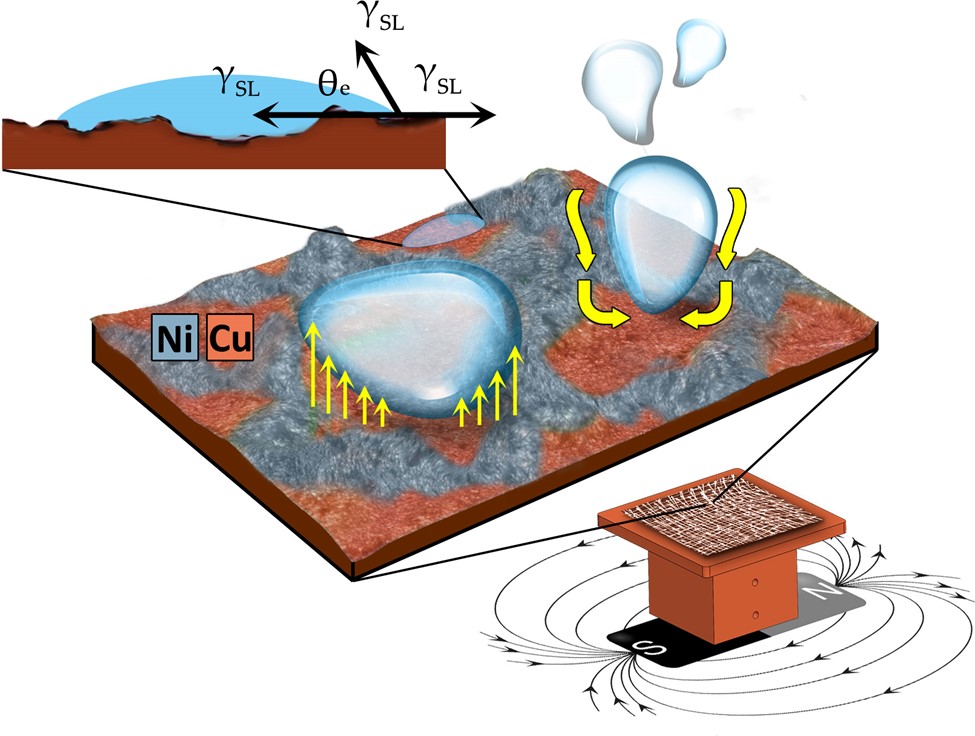
We present enhanced phase change heat transfer achieved by magnetically aligned nickel precursor inks on copper substrates. Alignment was performed in single direction and grid orientation. Pool boiling studies were performed to obtain correlations between the heat flux, heat transfer coefficients and wall super heat. The effects of surface wettability and roughness on nucleate boiling heat transfer properties, and bubble dynamics is reported. Our studies yielded a critical heat flux (CHF) of 185.9 W/cm² and a heat transfer coefficient (HTC) 106.9 kW/m² °C for water on Ni grid patterned surface, representing an improvement of 49.9% in CHF and 105% in HTC compared to plain copper surface. The alignment of nickel followed by its sintering introduced nucleation characteristics that improved bubble dynamics. This is attributed to a) altered three-phase contact angle via chemically heterogeneity of Ni/Cu surface, and b) microlayer evaporation of confined fluids in the rough surfaces.