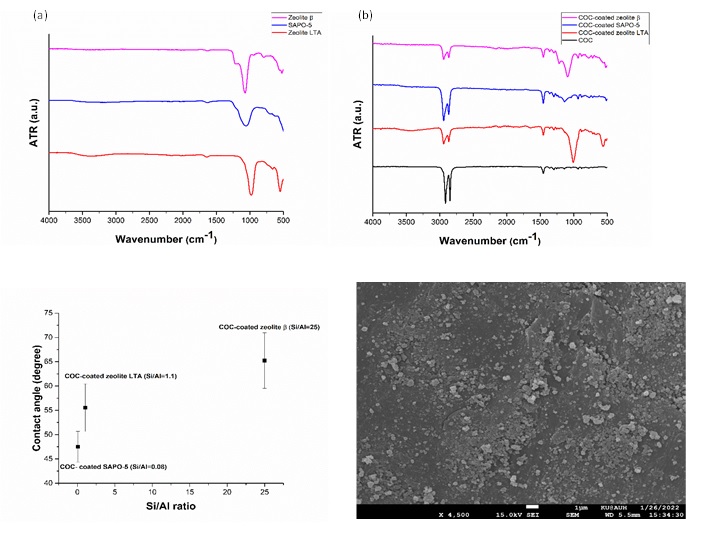
Immobilization of zeolite nanoparticles has attracted great interest in various potential applications such as catalysis and membrane separations[1, 2], chemical sensors[3], and microfluidic devices[4]. Self-assembly method can be used to immobilize zeolite crystal grains on different substrates through chemical linkages including the
ionic, covalent and intermolecular bonds between the zeolite crystals and the substrate to form a film with good uniformity. In the present work, zeolite crystals were immobilized on a cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) using a simple wet-chemical surface treatment. During the chemical surface treatment, the hydrophilic silane 3-aminopropyl) triethoxy (APTES) was used to form covalent bonds between the zeolite crystals and the polymer surface, resulting in the formation of zeolite films with good uniformity. Three types of zeolites including zeolite LTA, zeolite β and SAPO-5 were used as model building blocks. Different characterization techniques such as FTIR, SEM and contact angle measurements were used to investigate the characteristics of COC-coated zeolites. The results confirmed the deposition of zeolite layers consisting of highly packed crystals on the COC surface, demonstrating good immobilization ability.
References:
[1] H. Jiang, B. Zhang, Y. S. Lin, and Y. Li, "Synthesis of zeolite membranes," Chinese Science Bulletin, vol. 49, no. 24, p. 2547, 2004/12/01 2004, doi: 10.1360/03wb0146.
[2] B. M. L. Dioos, B. F. Sels, and P. A. Jacobs, "Chapter 25 - Catalyst Immobilization on Inorganic Supports," in Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, vol. 168, J. Äejka, H. van Bekkum, A. Corma, and F. Schüth Eds.: Elsevier, 2007, pp. 915-XXVI.
[3] F. Almazán et al., "Zeolite based microconcentrators for volatile organic compounds sensing at trace-level: Fabrication and performance," Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, vol. 26, p. 084010, 08/01 2016, doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/26/8/084010.
[4] X. Huang, G. Zhang, L. Zhang, and Q. Zhang, "Continuous Flow Synthesis of a ZSM-5 Film in Capillary Microchannel for Efficient Production of Solketal," ACS Omega, vol. 5, no. 33, pp. 20784-20791, 2020/08/25 2020, doi: