2022 Annual Meeting
(673e) A Mathematical Model to Predict the Drug Release Profile in a Single-Layered Osmotic Controlled Release Tablet
Authors
In this study, a single-layered osmotic controlled release tablet, which is conventionally also known as an Extrudable Core System (ECS), is modelled in order to accurately predict the drug release rate as a function of several key parameters. These include, the excipients and the active pharmaceutical ingredient, the coating thickness as well as the geometry of the tablet. The model elucidates the key events occurring during the dissolution of a tablet, which is coated with a semi-permeable membrane. These events include, the solvent influx, which is driven by the osmotic pressure differences across the coating, core component (drug, polymer and osmogen) dispersion, tablet swelling due to the solvent accumulation, the hydrostatic pressure build up within, tensile stresses acting on the coating, the extrusion of the dispersed core components and dissolution of the drug particles in bulk. Additionally, the condition for successful entrainment of the drug particles based on the hydrated phase viscosity and other parameters has been derived. The model is validated by comparing the predictions with drug release data for two drugs of differing solubility. The predicted release and the measurements agree well thus confirming the suitability of our model in describing the osmotically controlled drug release process from ECS tablets.
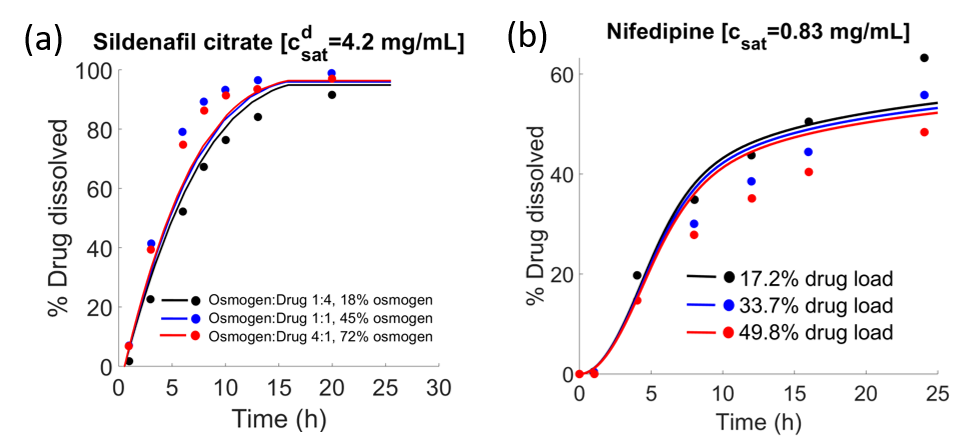
The attached figure compares the predicted drug release profile with measurements, (a) Effect of osmogen concentration on drug release, and (b) Effect of drug concentration on drug release. The solid lines are model predictions while the symbols represent measurements.