Page 267 - CHEF Guide
P. 267
Risk Analysis and Risk Assessment
Societal Risk addresses the number of people who may be affected by hazardous incidents. Societal risk expresses
the cumulative risk to groups of people who might be affected by such events. Societal risk measures the potential for
impacts to a group of people located in the effect zone of an incident or set of incidents. Thus, societal risk estimates include
a measure of incident scale in terms of the number of people impacted (or estimated fatalities).
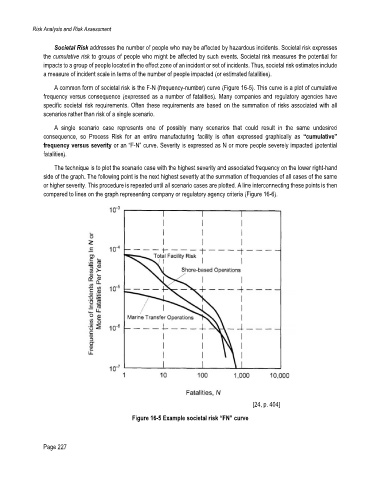
A common form of societal risk is the F-N (frequency-number) curve (Figure 16-5). This curve is a plot of cumulative
frequency versus consequence (expressed as a number of fatalities). Many companies and regulatory agencies have
specific societal risk requirements. Often these requirements are based on the summation of risks associated with all
scenarios rather than risk of a single scenario.
A single scenario case represents one of possibly many scenarios that could result in the same undesired
consequence, so Process Risk for an entire manufacturing facility is often expressed graphically as “cumulative”
frequency versus severity or an “F-N” curve. Severity is expressed as N or more people severely impacted (potential
fatalities).
The technique is to plot the scenario case with the highest severity and associated frequency on the lower right-hand
side of the graph. The following point is the next highest severity at the summation of frequencies of all cases of the same
or higher severity. This procedure is repeated until all scenario cases are plotted. A line interconnecting these points is then
compared to lines on the graph representing company or regulatory agency criteria (Figure 16-6).
[24, p. 404]
Figure 16-5 Example societal risk “FN” curve
Page 227