Page 113 - CHEF Guide
P. 113
Experience and Historical Incidents
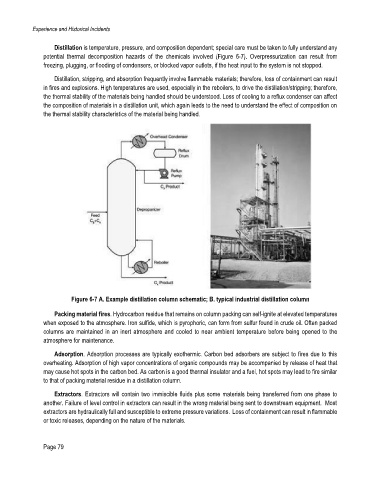
Distillation is temperature, pressure, and composition dependent; special care must be taken to fully understand any
potential thermal decomposition hazards of the chemicals involved (Figure 6-7). Overpressurization can result from
freezing, plugging, or flooding of condensers, or blocked vapor outlets, if the heat input to the system is not stopped.
Distillation, stripping, and absorption frequently involve flammable materials; therefore, loss of containment can result
in fires and explosions. High temperatures are used, especially in the reboilers, to drive the distillation/stripping; therefore,
the thermal stability of the materials being handled should be understood. Loss of cooling to a reflux condenser can affect
the composition of materials in a distillation unit, which again leads to the need to understand the effect of composition on
the thermal stability characteristics of the material being handled.
Figure 6-7 A. Example distillation column schematic; B. typical industrial distillation column
Packing material fires. Hydrocarbon residue that remains on column packing can self-ignite at elevated temperatures
when exposed to the atmosphere. Iron sulfide, which is pyrophoric, can form from sulfur found in crude oil. Often packed
columns are maintained in an inert atmosphere and cooled to near ambient temperature before being opened to the
atmosphere for maintenance.
Adsorption. Adsorption processes are typically exothermic. Carbon bed adsorbers are subject to fires due to this
overheating. Adsorption of high vapor concentrations of organic compounds may be accompanied by release of heat that
may cause hot spots in the carbon bed. As carbon is a good thermal insulator and a fuel, hot spots may lead to fire similar
to that of packing material residue in a distillation column.
Extractors. Extractors will contain two immiscible fluids plus some materials being transferred from one phase to
another. Failure of level control in extractors can result in the wrong material being sent to downstream equipment. Most
extractors are hydraulically full and susceptible to extreme pressure variations. Loss of containment can result in flammable
or toxic releases, depending on the nature of the materials.
Page 79