(348f) Rapid Bioproduction of Protein Biologics Using Plants in Response to Sars-Cov-2
AIChE Annual Meeting
2022
2022 Annual Meeting
Topical Conference: Chemical Engineers in Medicine
Pandemic Response and Public Health
Tuesday, November 15, 2022 - 2:18pm to 2:39pm
Methods: Romaine lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. longifolia) and control N. benthamiana were transfected by particle bombardment; recombinant protein production dynamics were compared to transformation by infiltration of A. tumefaciens. Production of target proteins in leaf tissue extract was identified by visualization on SDS-PAGE and Western blot. The transgene for the protein of interest, the receptor-binding domain protein (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2, was labeled with a His-tag and inserted into a geminiviral vector for rapid production in the plant hosts and used in both particle bombardment and agroinfiltration methods for transient expression.
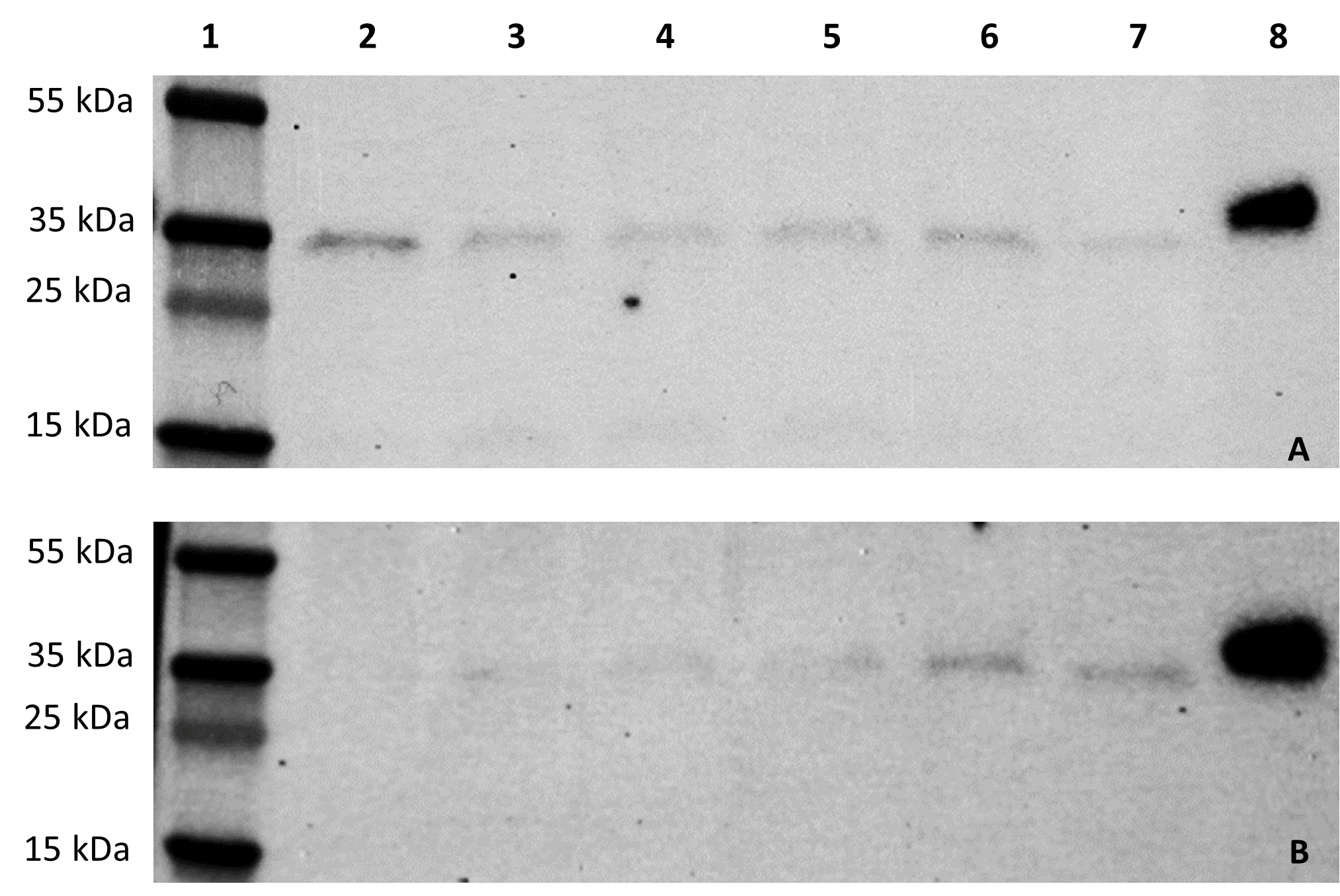
Results: From the studies, it was identified that bombarded tissue displays variations in protein production depending on age of the plant or growth of the leaf. A. tumefaciens infiltration protein dynamics indicate that the genetic construct can efficiently be expressed in both hosts within 24 hours, with N. benthamiana expressing the protein of interest in as little as 4 hours (Fig. 1).
Implications: While the production of RBD is the focus of this study, the platform is designed to be applicable to produce other protein-based therapeutics and diagnostics within 24 hours. RBD is a valuable initial target as it can be used for screening antibodies and additional therapeutics for diagnostics to combat COVID-19, thus the low-cost and large-scale production of this biologic is imperative. The next step for this project would be to construct a viral vector for systemic infection within the host plants for rapid and enhanced bioproduction of target proteins. This technology has the potential to allow for a mobile therapeutic production system that can be rapidly deployed with limited need for external resources, decreased specialized training for processing, and a large reduction in waste compared to current production platforms.
Figure 1. Time study of agroinfiltrated progression of RBD production in N. benthamiana (A) and romaine (B). Lanes 1: protein standard ladder; 2: 4-hours post infiltration (HPI); 3: 8 HPI; 4: 12 HPI; 5: 16 HPI; 6: 20 HPI; 7: wild type plant crude extract; 8: RBD-His positive control, 30ng. Western blot probed with mouse anti-His antibody at a concentration of [1ng/uL] followed by anti-mouse-HRP at [0.1ng/uL].