(167l) Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Mercury Adsorption By Porous Sulfur Copolymers
AIChE Annual Meeting
2022
2022 Annual Meeting
Materials Engineering and Sciences Division
Poster Session: Materials Engineering & Sciences (08A - Polymers)
Monday, November 14, 2022 - 3:30pm to 5:00pm
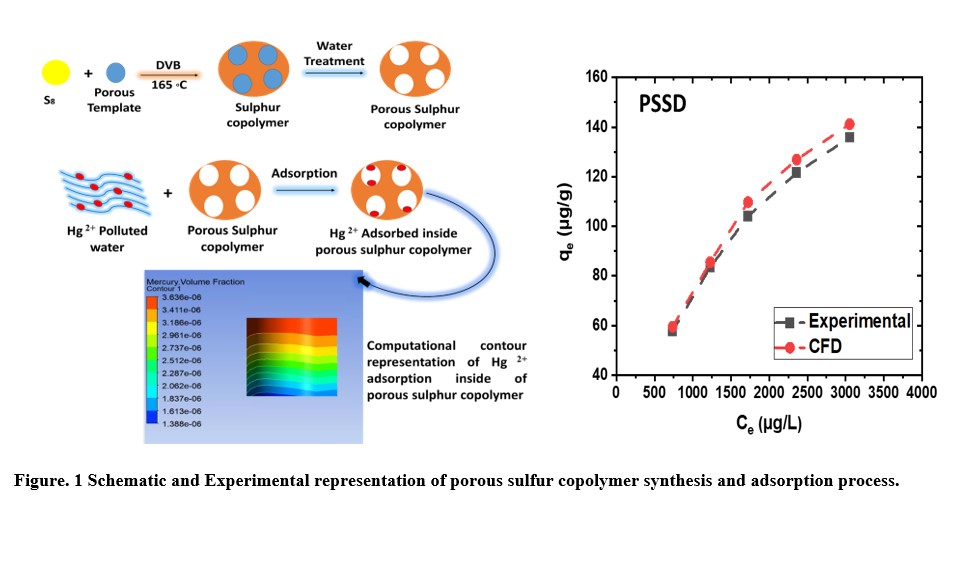
The computational fluid dynamic analysis of mercury adsorption explained through ANSYS Fluent software for porous sulfur copolymers. The hydrodynamics of wastewater has explained by considering the laminar flow porous zone model for mercury ion adsorption under the independent grid process. The different process parameters examined such as mercury ion concentrations, volumetric flowrate of wastewater, temperature, and bed height of adsorbent material to optimize the process conditions at high adsorption capacities for industrial level. During the computational analysis mass imbalance, and stress-strain parameters remain constant. The CFD simulated results validated the experimental results an predicted the results by changing the process parameters. The PSSD sample presenting the porous sulfur cross-linked foam prepared by using poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) as a porogen. It has high porosity (59.09%), less density (0.53 g/cm3), and smaller particle size (20-50 µm); so, it shows high absorption capacity in both cases experimental and CFD simulations. The CFD Ansys simulation approach employ to introduce a new perspective to validate lab scale results and predict the results at large scale. This technique can help to scaleup the sulfur foam production in bulk quantity.