(344c) Evaluation of Chromium Sites in Cr/ZSM-5 for Ethane Dehydrogenation
AIChE Annual Meeting
2020
2020 Virtual AIChE Annual Meeting
Catalysis and Reaction Engineering Division
Poster Session: Advances in Zeolite Science and Technology
Friday, November 20, 2020 - 8:00am to 9:00am
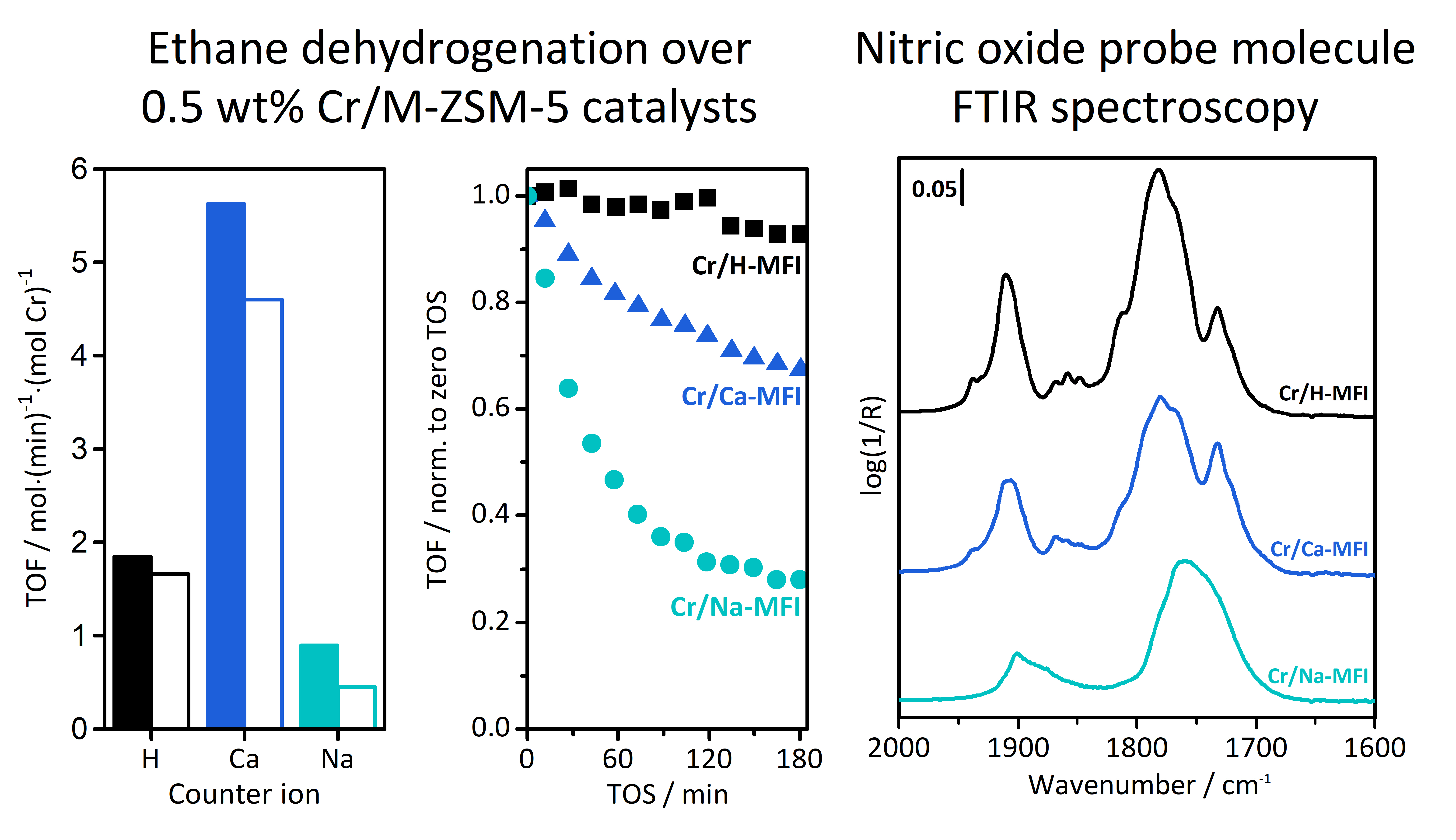
Zeolite-supported metal catalysts present opportunities to gain fundamental understanding of industrially relevant catalysts as well as to develop catalysts with new or optimized properties. Zeolite surfaces provide precise binding sites for supported metals, resulting in active sites that are amenable to precise characterization. Probe molecule Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a powerful tool to provide information about the electronic and coordinative states of dispersed metals on zeolite surfaces. FTIR with nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO) probe molecules was effective in distinguishing various types of reduced Cr species present in Cr/H-ZSM-5 (Si/Al 15) samples with varying Cr loading (0.27-1.6 wt%). Characterization by FTIR and X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy (XANES) was related to catalytic performance in ethane dehydrogenation to provide insight into design principles for improved Cr/zeolite catalysts for ethane conversion. It was found that in 0.5 wt% Cr/H-ZSM-5, reduction of Cr occurred under N2 flow at dehydrogenation reaction temperature (650 oC), and that exposure to ethane at this temperature provoked no further change in the state of Cr. Correspondingly, this catalyst displayed stable ethane dehydrogenation activity under reaction conditions. The presence of zeolite framework Al sites was necessary to stabilize active Cr sites during ethane dehydrogenation. In the absence of available Al sites, Cr sites deactivated quickly. With increasing Cr/Al molar ratio, greater abundance of electron-rich Cr2+ species existed after reduction. The resulting catalysts were more active for ethane dehydrogenation but activity was less stable with time on stream. The accompanying Figure compares ethane dehydrogenation activity and NO-DRIFTS spectra for Cr/M-ZSM-5 samples differing in exchanged extra-framework cation (M = H+, Na+, Ca2+). The results suggest that not only the availability, but also the proximity to one another, of framework Al sites influences the state of reduced Cr and the activity of Cr/ZSM-5 catalysts.

Topics
Checkout
This paper has an Extended Abstract file available; you must purchase the conference proceedings to access it.
Do you already own this?
Log In for instructions on accessing this content.
Pricing
Individuals
| AIChE Pro Members | $150.00 |
| AIChE Emeritus Members | $105.00 |
| AIChE Graduate Student Members | Free |
| AIChE Undergraduate Student Members | Free |
| AIChE Explorer Members | $225.00 |
| Non-Members | $225.00 |
