(320c) CFD-IBM-DEM Analysis of PM Filtration in Fluidized Bed Based on Force Balance to Evaluate Operation Conditions.
AIChE Annual Meeting
2020
2020 Virtual AIChE Annual Meeting
Particle Technology Forum
Particulate Systems Dynamics and Modeling: Discrete and Continuum Approaches
Thursday, November 19, 2020 - 8:30am to 8:45am
In this study, numerical simulation of PM filtration was conducted via CFD-IBM (immersed boundary method)-DEM [3] to consider the effect of accurate flow around bed particle. The effects of operating conditions are assessed based on forces acting on PM and the ratio of captured PM number to total PM number. The schematic diagram of numerical method is shown in Figure. Since the method requires highly computational cost, a part of bed particle layer was demonstrated. In the following figure, grey particle is bed particle and PM is blue particle. The diameters of bed particle and PM are 420 and 2 µm, respectively. PM is supplied from bottom of bed particle layer at feed rate of 100 per 0.0001 seconds, and initial velocity is same as superficial velocity. The most PM collides with bed particle, and it is captured on bed particle surface by adhesion force. The collection efficiency is about over 90% at superficial velocity of 0.4 m/s. The highly collection efficiency is obtained even at higher gas velocity of 0.8 m/s when bed particle is about closed packed. This gas velocity is twice of 0.4 m/s at which collection efficiency of 100% is obtained in previous experimental work [1]. The cohesive interaction between PM-bed particle or PM-PM is dominant force for fine particle. It makes collection efficiency high, and PM is stably maintained on bed particle by adhesion force.
[1] T. Yamamoto, K. Hori, J. Tatebayashi, An experimental investigation of the PM adhesion characteristics in a fluidized bed type PM removal device, Powder Technol., 289, 2016, 31-36.
[2] K. Yokoo, T. Yamamoto, H. Matsune, M. Kishida, J. Tatebayashi, CFD-DEM analysis of PM filtration due to adhesion force using fluidized bed, 18th Asian pacific confederation of chemical engineering, 2019, B321
[3] T. Kajishima, S. Takiguchi, Interaction between particle clusters and particle-induced turbulence, Int. J. Heat and Fluid Flow, 23, 2002, 639-646.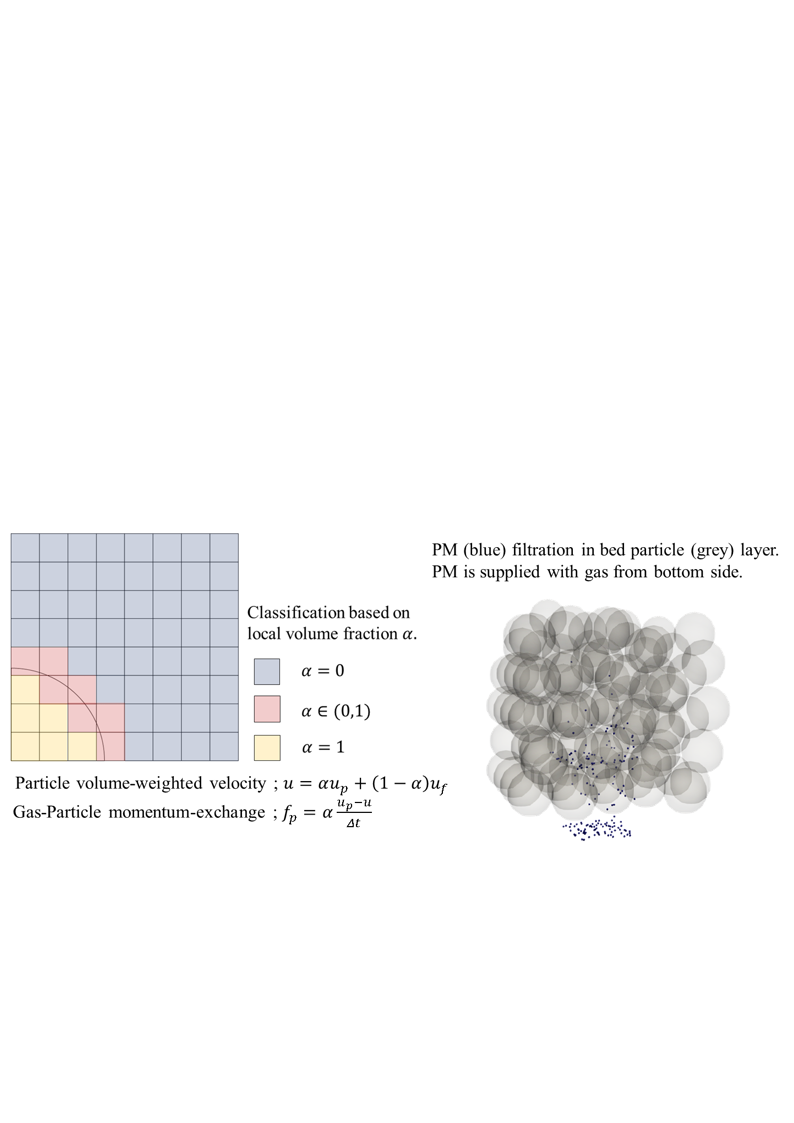
Checkout
This paper has an Extended Abstract file available; you must purchase the conference proceedings to access it.
Do you already own this?
Log In for instructions on accessing this content.
Pricing
Individuals
| AIChE Pro Members | $150.00 |
| AIChE Emeritus Members | $105.00 |
| AIChE Graduate Student Members | Free |
| AIChE Undergraduate Student Members | Free |
| AIChE Explorer Members | $225.00 |
| Non-Members | $225.00 |
